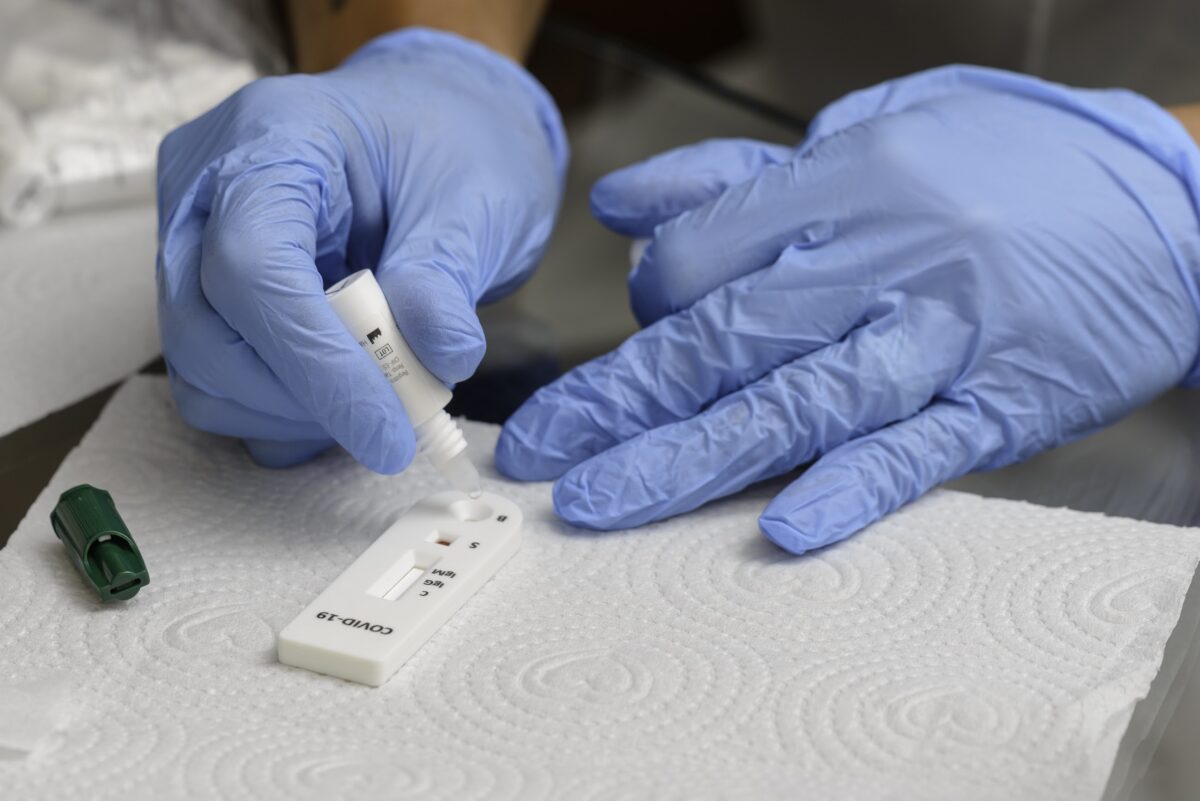
Rapid tests are a fast and accurate way to diagnose patients in a primary healthcare setting
Global partnership feeds healthy supply of rapid COVID-19 tests to low- and middle-income countries
A set of global agreements reached in September 2020 paved the way for 120 million rapid COVID-19 tests to be distributed to low and middle-income countries.
The Access to COVID-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator, working with other organizations, concluded these agreements to enable the manufacture, distribution and rollout of these vital diagnostic tools.
At the time, there was a huge unmet need for fast diagnostic testing globally, especially in the low and middle-income bracket.
The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC), the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), the Global Fund, Unitaid, and World Health Organization (WHO) all worked on this project.
There was a particular focus on making tests available to countries without extensive laboratory facilities or trained health workers to implement molecular (polymerase chain reaction or PCR) tests.
Why is testing crucial in the fight against COVID-19?
Rapid tests are a fast and accurate way to diagnose patients in a primary healthcare setting, as this is where most people access services.
Rapid tests are also cheaper than laboratory tests. With a fast initial diagnosis, track and trace teams in more remote and rural areas can start work sooner without waiting for laboratory test results.
Quick results can prevent the virus from spreading in communities. Rural and remote healthcare settings especially need access to rapid testing, as accessing centralized laboratory services can take a long time.
Procurement
The Global Fund made $50-million available to purchase 10 million tests per country.
Distribution
FIND and WHO supported countries in distributing these tests.
Unitaid and the Africa CDC combined resources rollout tests to countries in Africa from October 2020.